Wednesday, January 28, 2015
Lesson 3 Direction of Light, Diffusion, Diffraction and Using One Light
Examples of diffusion





What happens when a point source (like the sun or our Halogen Bulb) falls on a solid white sphere:
1. A highlight is created
2. A cast shadow is created
3. A core is created in the transition of the highlight and the shadow
4. A cast shadow is created
5. A specular or incident highlight is created with the highlight (it is the direct reflection of the light source)

The cube is tilted to reveal 3 sides equally. When a point source (our Halogen bulb) is placed over and as close to the camera lens as possible, all three sides reflect equally. When the light is moved to the left and up, the 3 sides reflect light in unequal ways and appear as 3 differentvalues
Thursday, January 22, 2015
Assignment 2 Demonstrate the 3 Laws of Light in One Photograph
In one photograph using one light source clearly demonstrate the 3 laws of light at work. Include the light source in the photograph. The subject is the light. Think of it as more of a physics project than a photograph. Use a dodging tool to prevent the light from flaring the lens. Try to crop out any rigging you might use and make the image about the light.
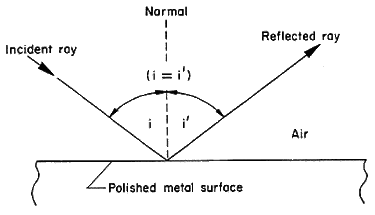
Lesson 2 Angle of Incidence Equal Angle of Reflection
Wednesday, January 14, 2015
Assignment 1 Inverse Square Law
1. Using 3 identical 4x5 grey cards set 1 foot apart, overlapping slightly and placed at a 45 degree angle from the camera angle. Make 4 photographs of the cards with the light 2 feet, 4 feet, 8 feet, 16 feet and 32 feet from the middle card. Use an incident meter on the middle card to give the correct exposure. The middle card should have the same value on each photograph. Use Lightroom to weak the middle card until they all read the same value.
2. Use 3 4x5 cards a black card in front, a grey card in the middle and a white card in the back. Using the same single point source make all 3 cards appear to be the same value. You can move the cards and the light source until it works.
3. Create a blog on blogger using your google account and use the simple template.
4. Send the url for your blog to ccs@nyc.rr.com by next Monday.
2. Use 3 4x5 cards a black card in front, a grey card in the middle and a white card in the back. Using the same single point source make all 3 cards appear to be the same value. You can move the cards and the light source until it works.
3. Create a blog on blogger using your google account and use the simple template.
4. Send the url for your blog to ccs@nyc.rr.com by next Monday.
Lesson 1 Inverse Square Law
The inverse square law states that the intensity of the light from a point source diminishes inversely to the square of the distance. I=1/d² Here is a better illustration that what I drew on the white board.
I got this next chart from Lee Varis's website. He illustrates here the relationship of 18% grey to a modified 10 step zone system, 50% that you would see in Lightroom's histogram and the number 118 you see in Photoshop's histogram using RGB color space.
Here is the results of our test in class with the middle grey card adjusted in Lightroom and tweaked in photoshop to look the same. You can see the Front card gets darker in relation to the Middle card as the light is moved further away and the Back card gets lighter as the light is moved further away.
Ben Kong's Version
Tuesday, January 13, 2015
Syllubus
Instructor: Chris Callis
The Laws of Light and How to Break Them
Spring 2015
Wednesday 3-5:50pm
Location: SVA MFA Photo Studio
Who should take this class:
Anyone interested in learning photographic lighting. No prior knowledge of lighting is required.
Class Description:
This course is an opportunity to learn the laws of light and to gain an appreciation of how important an understanding of light is to a photographer’s process. The class will begin with an exploration of the physics of light in order to explain its behavior. The weekly sessions and assignments will teach the student how to approach every lighting experience with confidence. The purpose is to master these concepts and to ensure effective application of this knowledge. The ability to problem solve is a crucial element when faced with challenging lighting situations and without this understanding it is very difficult to move beyond obvious limitations. The ultimate goal is to be able to apply these concepts and then to see all the possibilities.
Assignments:
Each week there will be a demonstration and a class exercise that will end with a weekly assignment. There will be a total of thirteen weekly assignments and one final project.
Each student will post their weekly assignments on their lighting blog along with a sketch and brief explanation of their results.
Grading:
A commitment from the students is expected. Being on time, prepared with homework and ready to learn are requirements. Active participation during the demonstrations is also required. The student’s aesthetic approach to lighting along with the blog presentation are factors in grading.
Schedule:
Lesson 1: Inverse Square Law
Lesson 2: Angle of Incident, Light Travels in a Straight Line
Lesson 3: One Light Source
Lesson 4: Three Light Source
Lesson 5: One Strobe
Lesson 6: Size Matters
Lesson 7: Strobe and Continuous Light
Lesson 8: Hand Flash
Lesson 9: Outdoor Flash
Lesson 10: Light Painting
Lesson 11: Shiny Metal and Glass
Lesson 12: Night Photography
Lesson 13: Stop Action
Lesson 14: Bring in a lighting problem to solve
Lesson 15: Review final assignment
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)